Fixed vs. Variable Income Securities: Which is Better for Your Investment Portfolio?
When it comes to investing, one of the biggest decisions you’ll face is whether to choose fixed income securities or variable income securities. Both types of investments have their pros and cons, and it’s important to understand the differences to make the best decision for your portfolio. Fixed income securities, such as bonds, offer a steady, reliable stream of income, while variable income securities, such as stocks, offer the potential for higher returns but also come with more risk. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the benefits and drawbacks of each type of investment and explore which may be the better choice for your investment strategy. So, if you’re wondering which type of income security is right for you, read on to learn more!
Understanding Fixed and Variable Income Securities
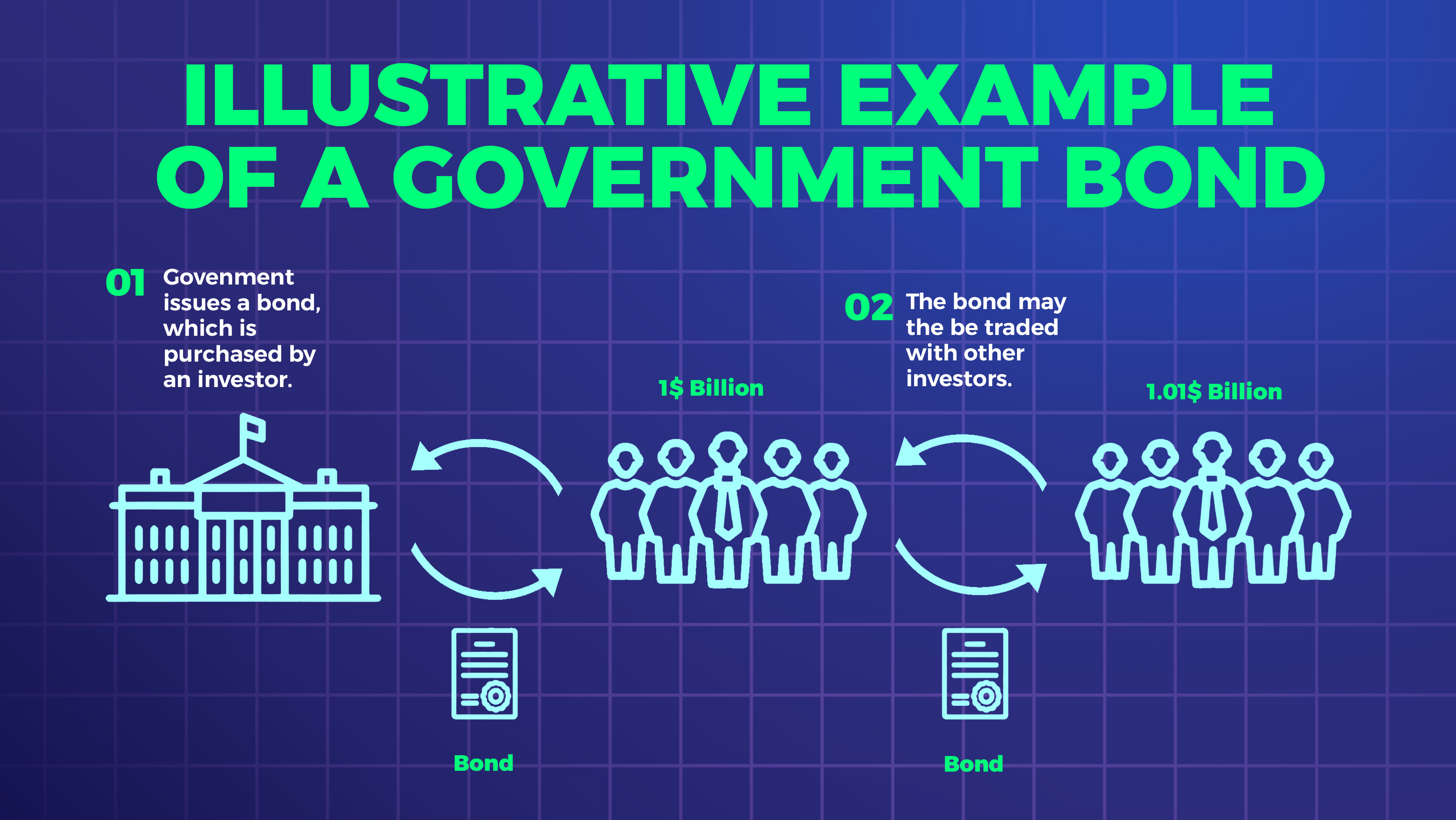
Fixed income securities are investments that offer a fixed rate of return over a specific period, such as bonds or certificates of deposits (CDs). These securities are usually considered low-risk investments because they provide a steady income stream and offer a predictable return on investment. In contrast, variable income securities, such as stocks, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), offer variable returns depending on the market’s performance.
Variable income securities are generally considered high-risk investments due to their fluctuating nature. However, these securities also offer the potential for higher returns over time, making them an attractive option for investors with a higher risk tolerance. It’s important to note that the value of these securities can fluctuate significantly in response to market conditions.
Benefits and Risks of Fixed Income Securities
Fixed income securities offer a range of benefits, including predictable income, capital preservation, and lower risk compared to variable income securities. These securities are an excellent choice for investors looking for a steady stream of income and those who wish to preserve their capital. However, investing in fixed income securities also has its drawbacks.
One of the most significant drawbacks of fixed income securities is that they typically offer lower returns compared to variable income securities, making them less attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Additionally, fixed income securities can be affected by inflation, which can erode the purchasing power of the income they generate.
Benefits And Risks Of Variable Income Securities
Variable income securities offer the potential for higher returns over time, making them an attractive option for investors who are willing to take on more risk. These securities can provide a diversified portfolio with exposure to different markets and industries, helping to spread out investment risk. However, there are also risks associated with variable income securities.
The most significant risk associated with variable income securities is market volatility. The value of these securities can fluctuate significantly in response to market conditions, leading to a potential loss of capital. Additionally, these securities can be affected by factors such as changes in interest rates, geopolitical events, and company-specific news.
Comparison of Returns for Fixed and Variable Income Securities
When it comes to returns, variable income securities have historically outperformed fixed income securities over the long term. However, this higher potential for returns comes with higher risk. Fixed income securities provide a reliable, steady stream of income, making them an excellent option for investors looking for a predictable source of income.
Investors should consider their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon when deciding between fixed and variable income securities. Those with a longer time horizon and higher risk tolerance may be willing to take on more risk with variable income securities, while those with a shorter time horizon and lower risk tolerance may prefer the stability of fixed income securities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Fixed and Variable Income Securities
When choosing between fixed and variable income securities, there are several factors to consider. These include investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and the current economic environment. Investors should also consider fees and expenses associated with each investment type and how they fit into their overall investment strategy.
It’s essential to understand that there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to choosing between fixed and variable income securities. The right choice depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance. It’s essential to work with a financial advisor to determine the best investment strategy for your unique needs.
Diversifying Your Investment Portfolio with Fixed and Variable Income Securities
Diversification is a key factor in building a successful investment portfolio. By investing in a mix of fixed and variable income securities, investors can spread their risk and potentially increase their returns. Fixed income securities provide stability and a reliable income stream, while variable income securities offer the potential for higher returns over time.
It’s essential to consider your investment goals and risk tolerance when diversifying your portfolio. A financial advisor can help you identify the right mix of securities to meet your needs.
Best Fixed Income Securities to Invest In
When it comes to investing in fixed income securities, there are several options available. Some of the best options include:
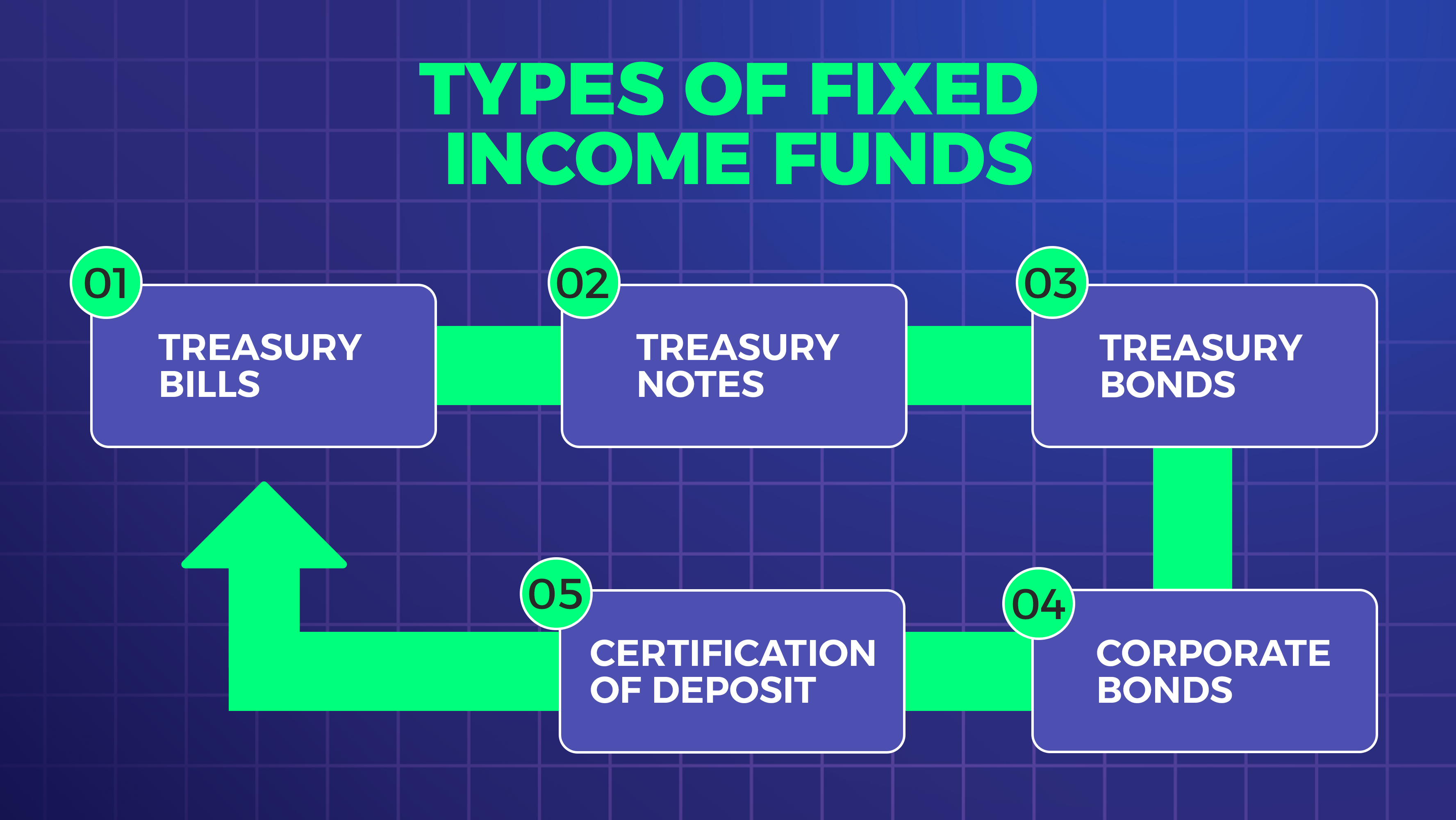
– US Treasury Bonds: These are considered some of the safest investments available and offer a reliable source of income.
– Municipal Bonds: These bonds are issued by state and local governments and offer tax advantages for investors.
– Corporate Bonds: These bonds are issued by companies and offer a higher yield than government bonds but come with more risk.
Working with a Financial Advisor to Choose the Right Securities for Your Portfolio
Choosing the right securities for your investment portfolio can be challenging. Working with a financial advisor can help you identify the right mix of fixed and variable income securities to meet your investment goals. A financial advisor can also help you navigate the complex world of investing and provide guidance and support as you build your portfolio.
Conclusion
Choosing between fixed and variable income securities can be challenging, but understanding the differences and benefits of each can help you make an informed decision. Investing in a mix of fixed and variable income securities can help you diversify your portfolio and potentially increase your returns. It’s essential to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon when choosing between fixed and variable income securities and to work with a financial advisor to build a successful investment strategy.