The Ultimate Guide to Fixed Income Securities: Exploring Types, Risks, and Returns
Are you looking for a stable and reliable investment option? Fixed income securities can be an excellent choice for investors looking to earn a steady income stream while minimizing risk. However, with so many different types of fixed income securities available in the market, it can be challenging to understand which one is right for you. That’s why we’ve put together the ultimate guide to fixed income securities. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the different types of fixed income securities, including bonds, treasury bills, and more. We’ll also examine the risks and returns associated with each type of security, helping you make informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to navigate the world of fixed income securities confidently. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of fixed income securities together!
Types of Fixed Income Securities
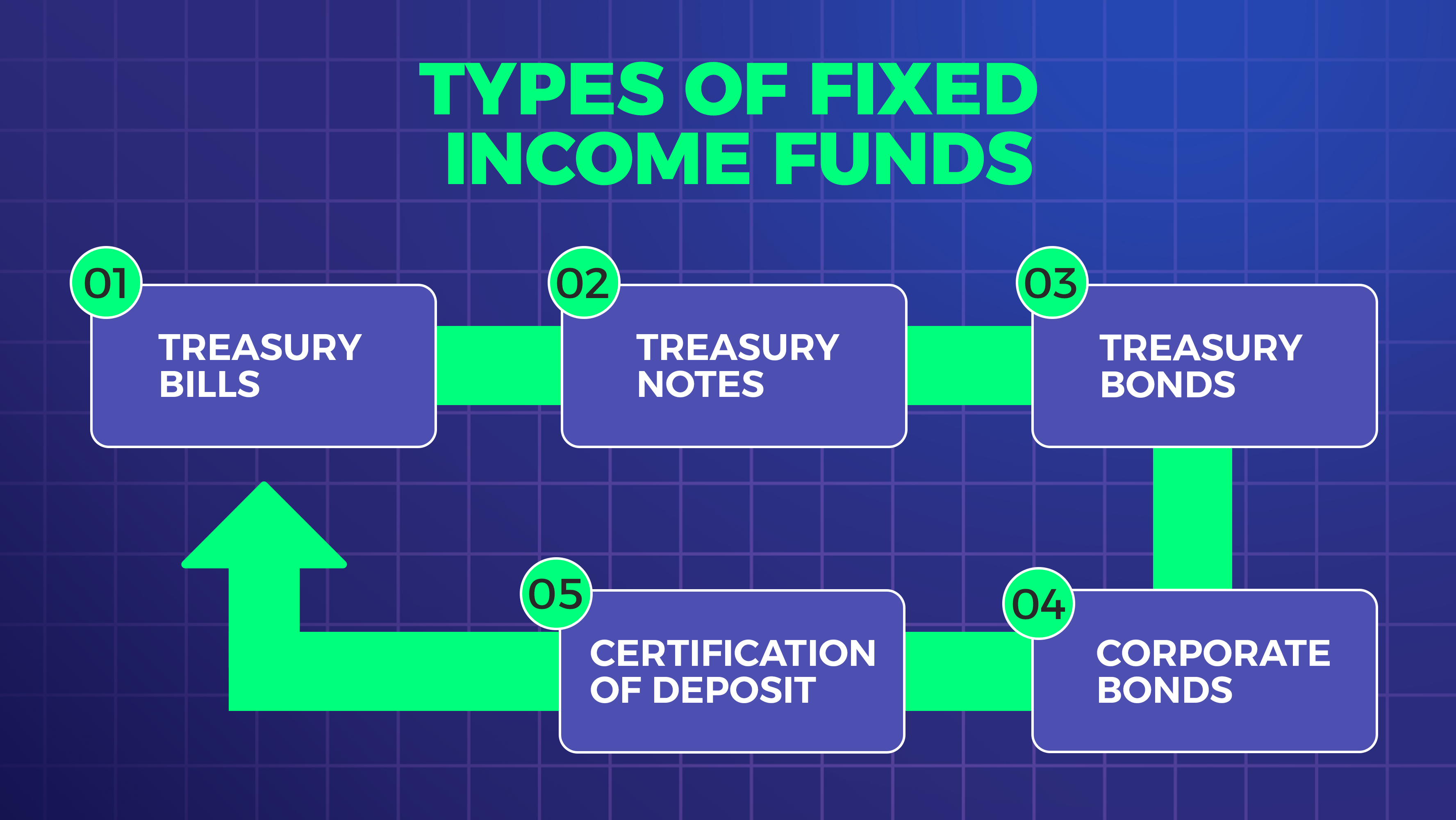
Fixed income securities are investments that offer a fixed return on investment over a set period. These securities are generally less risky than equities, making them an attractive option for investors looking for a steady income stream. The most common types of fixed income are bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market funds.
Bonds:
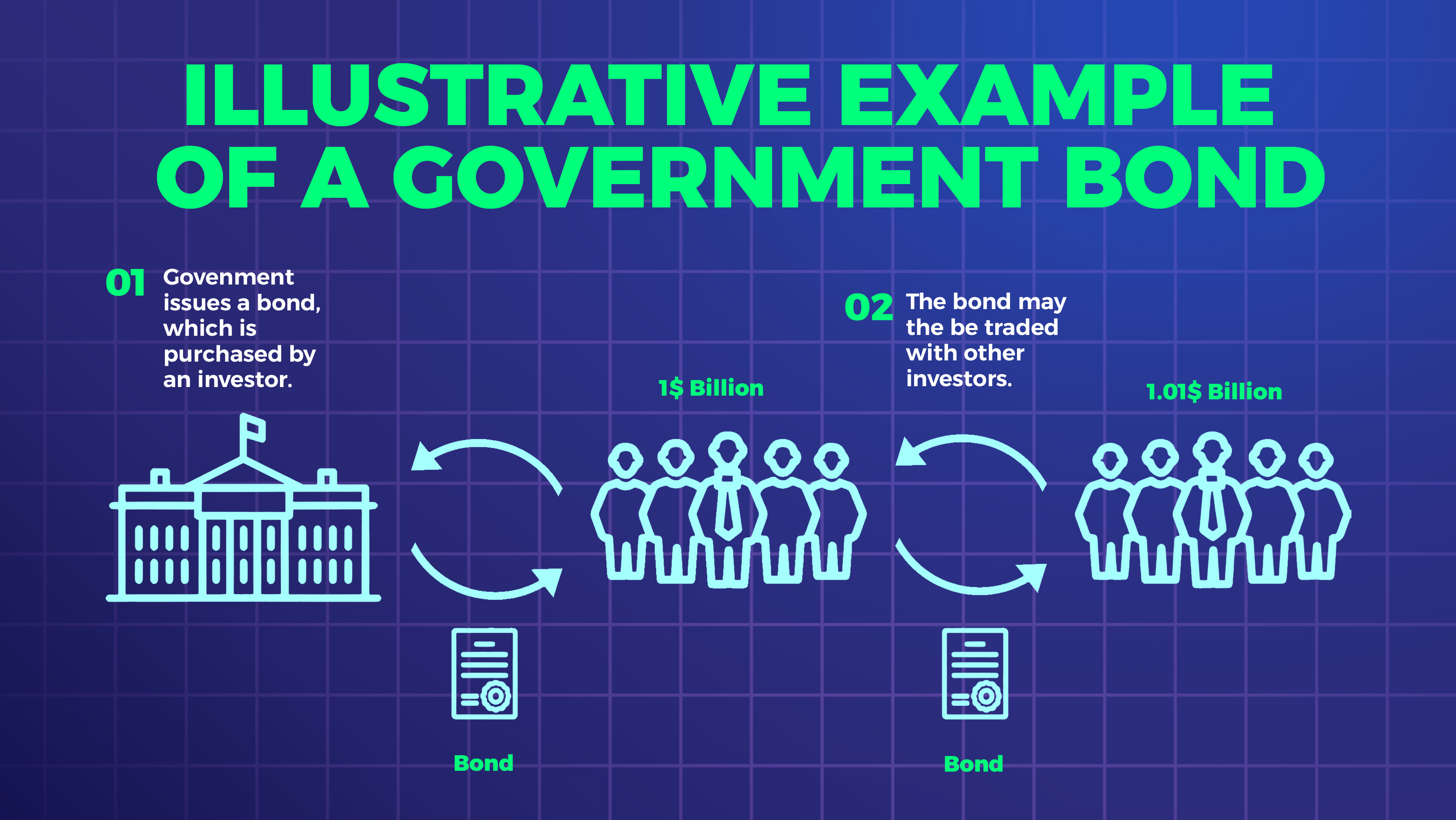
Bonds are a type of fixed income security that is issued by governments, corporations, and other entities. They are essentially loans that are made to these entities, and in exchange, investors receive regular interest payments until the bond’s maturity date. Bonds can be further classified into government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds. Government bonds are issued by the government to raise money, while corporate bonds are issued by companies to finance their operations. Municipal bonds are issued by local governments to raise funds for public projects.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs):
CDs are issued by banks and other financial institutions. They are a type of savings account that pays a fixed interest rate over a set period. CDs are FDIC-insured, which means that the principal amount invested is safe. However, if you withdraw your money before the CD matures, you may have to pay a penalty.
Money Market Funds:
Money Market Funds are mutual funds that invest in short-term debt securities such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. These funds are generally considered to be low-risk investments, but they may not offer a high return on investment.
Unlock Wealth: Sign Up Now for Smart Investing Success
Risks Associated with Fixed Income Securities
While fixed income securities are generally considered to be less risky than equities, there are still risks associated with them. Some of the most common risks associated with fixed income are credit risk, interest rate risk, and inflation risk.
Credit Risk
Credit Risk is the risk that the issuer of the fixed income security will default on their payments. This risk is higher for corporate bonds than for government bonds since companies are more likely to default on their debt than the government.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest Rate Risk is the risk that the value of the fixed income security will decrease if interest rates rise. This is because when interest rates rise, the value of existing fixed income securities decreases, as investors can earn a higher return on their money by investing in new securities that offer a higher interest rate.
Inflation Risk
Inflation Risk is the risk that the purchasing power of the fixed income security will decrease due to inflation. This is because inflation erodes the value of money over time, which means that the fixed income security may not be able to keep pace with inflation.
Understanding Bond Ratings
Bond ratings are a measure of the creditworthiness of the issuer of the bond. These ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies such as Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch. Bonds with higher ratings are considered to be less risky than bonds with lower ratings.
The highest bond rating is AAA, which is assigned to bonds that are considered to be of the highest quality and have the lowest risk of default. Bonds with a rating of BBB or higher are considered to be investment-grade bonds, while bonds with a lower rating are considered to be high-yield or junk bonds.
When investing in bonds, it’s important to consider the bond rating, as this can help you assess the risk associated with the investment.
Factors Affecting Fixed Income Returns
The returns on fixed income securities are influenced by a variety of factors, including the interest rate environment, the creditworthiness of the issuer, and the maturity of the security.
Interest Rates:
The returns on fixed income are generally influenced by the prevailing interest rates. When interest rates rise, the returns on fixed income also rise to keep pace with the new interest rates.
Creditworthiness :
The creditworthiness of the issuer of the fixed income security is an important factor in determining the return on investment. Higher-rated bonds typically offer lower returns than lower-rated bonds since they are considered to be less risky.
Maturity:
The maturity of the fixed income security also influences the return on investment. Longer-term securities generally offer higher returns than shorter-term securities since investors are giving up their money for a longer period.
Yield Curve Analysis
The yield curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the yield and maturity of fixed income. The yield curve is an important tool for fixed income investors, as it can provide insight into the future direction of interest rates.
A normal yield curve is upward-sloping, which means that longer-term securities offer higher yields than shorter-term securities. An inverted yield curve is downward-sloping, which means that shorter-term securities offer higher yields than longer-term securities. An inverted yield curve is generally considered to be a sign of an impending recession.
Fixed Income Investment Strategies
There are several investment strategies that investors can use when investing in fixed income. One of the most popular strategies is to create a laddered portfolio of bonds. This involves investing in a portfolio of bonds with different maturities, which can help to reduce the impact of interest rate changes on the portfolio.
Another popular strategy is to invest in bond mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These funds invest in a portfolio of bonds, which can help to reduce the risk associated with investing in individual bonds.
Tips for Investing in Fixed Income Securities
Here are some tips for investing in fixed income:
1. Diversify your portfolio by investing in a variety of different types of fixed income.
2. Consider investing in bond mutual funds or ETFs to reduce the risk associated with investing in individual bonds.
3. Research the creditworthiness of the issuer before investing in a bond.
4. Consider the maturity of the fixed income security before investing, as longer-term securities generally offer higher returns.
5. Monitor the yield curve to gain insight into the future direction of interest rates.
Fixed Income Securities vs. Equities
Fixed income are generally considered to be less risky than equities since they offer a fixed return on investment over a set period. However, fixed income securities may not offer the same potential for high returns as equities.
Equities are investments in stocks or shares of a company. These investments offer the potential for high returns, but they are also considered to be more risky than fixed income securities.
When deciding between fixed income securities and equities, it’s important to consider your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
Fixed income securities can be an excellent option for investors looking for a stable and reliable income stream while minimizing risk. By understanding the different types of fixed income securities, the risks associated with them, and the factors that influence returns, investors can make informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, the tips and strategies outlined in this guide can help you navigate the world of fixed income securities with confidence.