Maximizing Your Wealth: The Benefits of Asset Management Strategies
Asset management is the process of managing a company’s or individual’s investments to achieve specific financial goals while minimizing risk.
This includes a range of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
Asset management typically involves working with a professional asset manager, who uses a variety of techniques to analyze financial data, identify opportunities for investment, and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources.
These decisions may involve selecting individual securities or investment products, setting investment strategies, and monitoring the performance of the portfolio over time.
Effective asset management requires a deep understanding of financial markets, investment products, and risk management techniques, as well as strong analytical and communication skills.
It is an important tool for individuals and businesses looking to grow their wealth, Manage their assets, and achieve their financial goals over the long term.
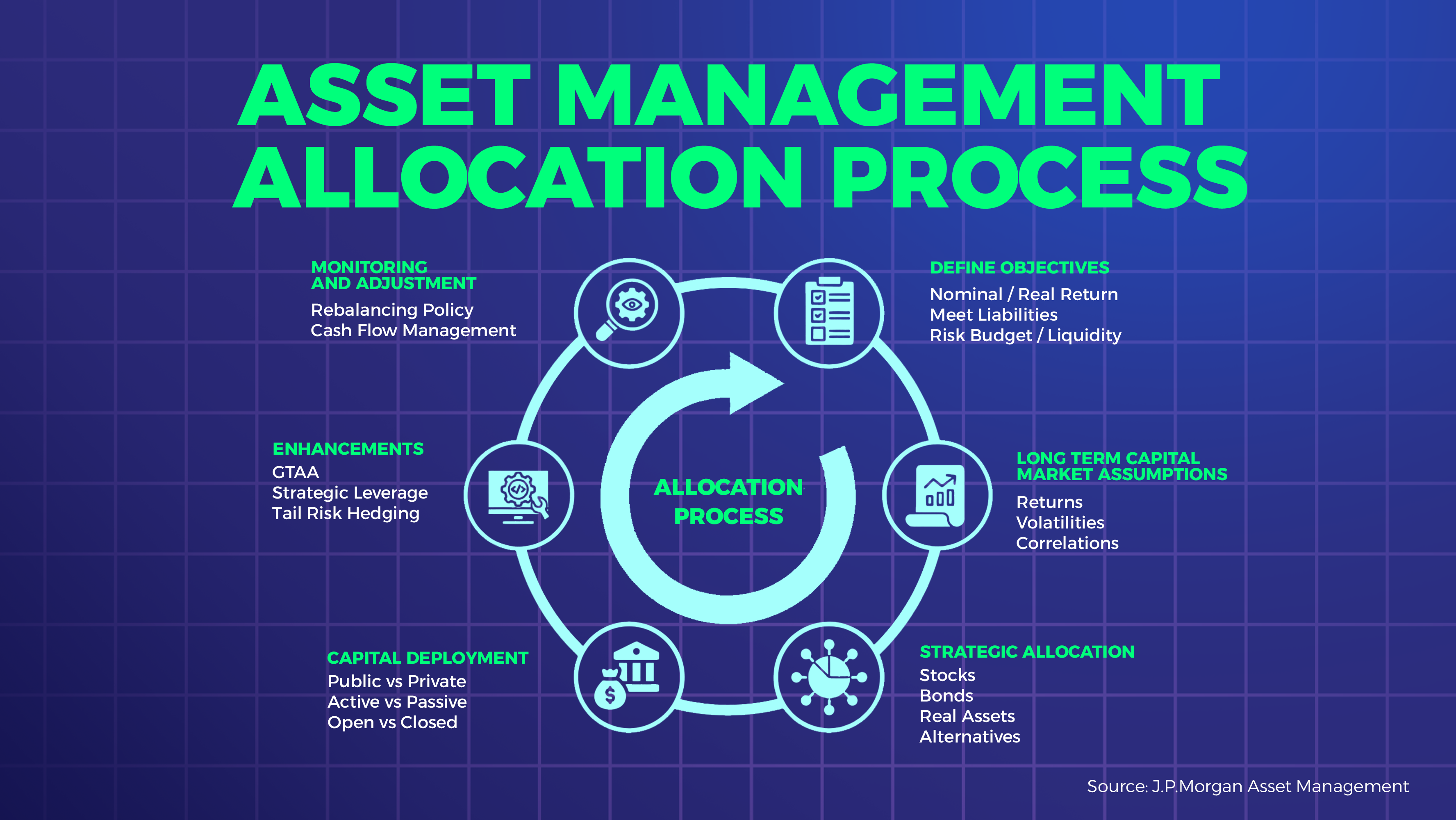
What is Asset Management Strategy?
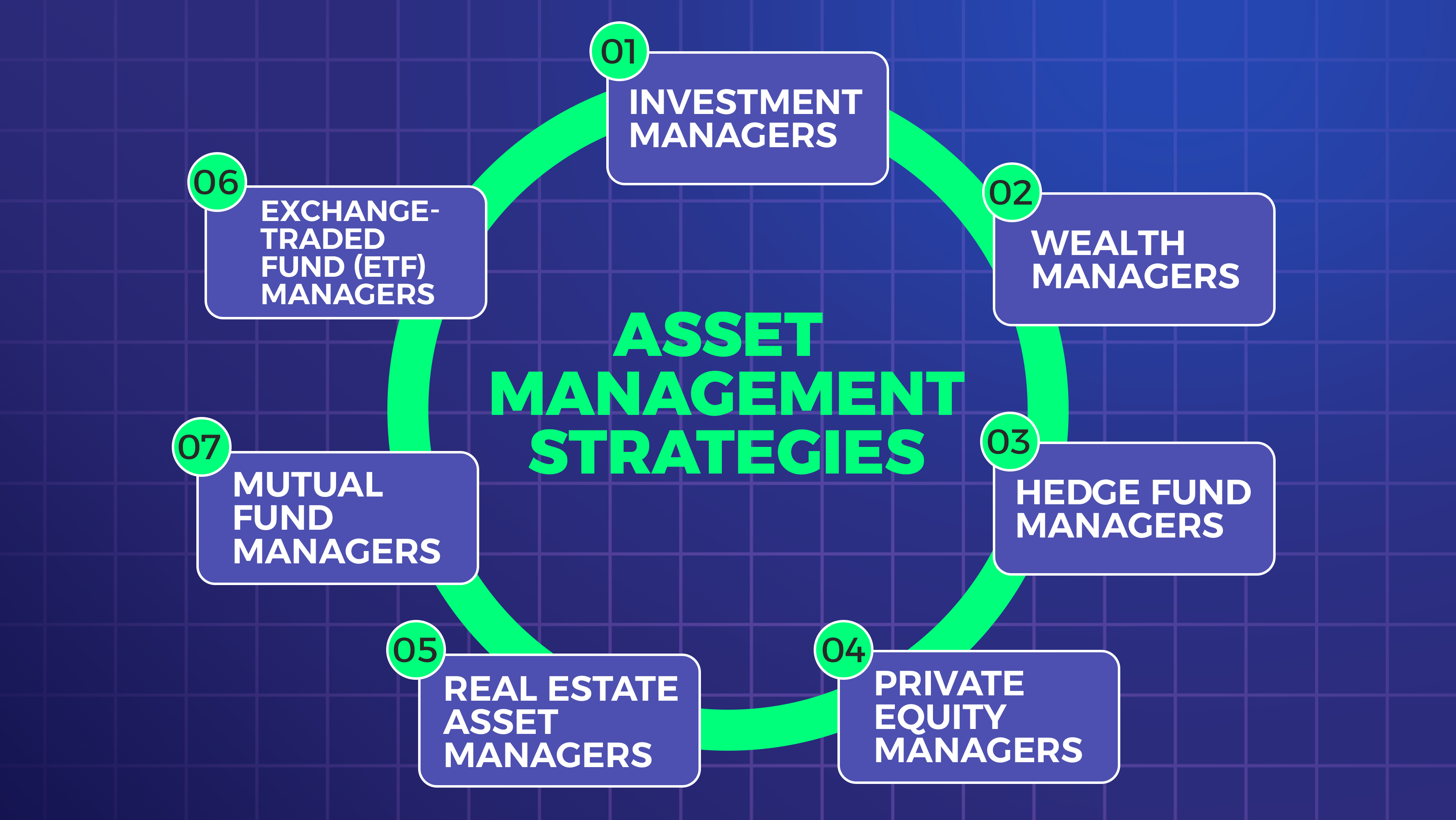
There are several types of asset managers, each specializing in managing different types of assets and catering to different types of clients.
Here are some of the most common types:
Investment Managers: These asset managers manage investment portfolios on behalf of their clients.
They are responsible for selecting individual securities and making investment decisions based on market analysis and their clients’ investment goals.
Wealth Managers: Wealth managers provide comprehensive financial planning and investment management services to high-net-worth individuals and families.
They help their clients manage their wealth by creating personalized investment strategies, tax planning, estate planning, and more.
Hedge Fund Managers: Hedge fund managers manage funds that invest in a variety of financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and derivatives.
They aim to generate high returns for their clients by using sophisticated investment strategies and taking on higher levels of risk.
Private Equity Managers: Private equity managers manage funds that invest in privately held companies.
They aim to generate high returns for their investors by buying and selling companies, restructuring businesses, and improving operational efficiency.
Real Estate Asset Managers: Real estate asset managers manage portfolios of real estate investments on behalf of their clients.
They are responsible for selecting properties, managing the properties, and maximizing their clients’ returns.
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) Managers: ETF managers create and manage ETFs, which are investment funds traded on stock exchanges.
They are responsible for selecting the underlying assets, managing the portfolio, and tracking the performance of the ETF.
Mutual Fund Managers: Mutual fund managers manage mutual funds, which are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets.
They are responsible for selecting the individual securities in the portfolio, managing the portfolio, and tracking the performance of the fund.
These are just a few examples of the types of asset managers that exist. Each type of asset manager has its unique set of skills, expertise, and investment strategies that cater to different types of clients and investment goals.
Unlock Wealth: Sign Up Now for Smart Investing Success
The Benefits of Asset Management Strategy
There are several benefits of asset management strategies that can help you achieve financial success. One of the primary benefits is risk management. Asset management strategies can help you diversify your investments, which can help reduce the risk of losses. By spreading your investments across different assets, you can minimize the impact of market fluctuations and reduce the risk of losing all of your investments in one fell swoop.
Another benefit of asset management strategies is that they can help you maximize your returns. By analyzing your investments and identifying opportunities for growth, you can take advantage of market trends and increase your returns over time. Asset management strategies can also help you save money on taxes by identifying tax-efficient investment strategies and reducing your tax liabilities.
Finally, asset management strategies can help you achieve your financial goals. By developing a comprehensive plan and sticking to it, you can ensure that you’re making progress towards your financial objectives. Whether you’re saving for retirement, paying off debt, or building a nest egg for your family, asset management strategies can help you get there.
Asset Management Statistics and Trends
Asset management is a rapidly growing industry, with more and more people turning to professional asset managers to help them achieve their financial goals. According to a recent report by PwC, the global assets under management (AUM) reached a record high of $101.7 trillion in 2019. This represents a 4.9% increase from the previous year and is expected to continue growing in the coming years.
Another trend in asset management is the rise of passive investing. Passive investing involves investing in a portfolio of assets that mirror a particular index, such as the S&P 500. This approach is becoming increasingly popular due to its low fees and ease of use. According to a report by Morningstar, passive funds accounted for 45% of all U.S. mutual fund and ETF assets in 2019, up from just 3% in 1995.
Types of Asset Management Strategies
There are several types of asset management strategies that you can use to manage your investments. One popular approach is value investing, which involves identifying undervalued assets and investing in them with the expectation that their value will increase over time. Another approach is growth investing, which involves investing in companies with high growth potential.
Another type of asset management strategy is income investing, which involves investing in assets that generate a steady stream of income, such as dividend-paying stocks and rental properties. This approach is popular among retirees and others who are looking for a reliable source of income.
Finally, there is the passive investing approach, which involves investing in a portfolio of assets that mirrors a particular index, such as the S&P 500. This approach is popular due to its low fees and ease of use, and is often used by those who want to minimize risk and maximize returns over the long term.
Choosing the Right Asset Management Strategy
Choosing the right asset management strategy depends on a variety of factors, including your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. If you’re looking for long-term growth, a growth or value investing approach may be best. If you’re looking for a reliable source of income, an income investing approach may be more appropriate. Ultimately, the best approach is one that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Creating an Asset Management Plan
Creating an asset management plan involves analyzing your current portfolio, identifying your financial goals, and developing a plan to achieve those goals. This process can be complex, and it’s often helpful to work with a financial advisor or asset manager to develop a comprehensive plan.
The first step in creating an asset management plan is to analyze your current portfolio. This involves identifying your current assets, determining their value, and assessing their performance. You should also consider your risk tolerance and investment timeline, as these factors will help you determine the appropriate asset management strategy.
Once you’ve analyzed your current portfolio, the next step is to identify your financial goals. This may include saving for retirement, paying off debt, or building a nest egg for your family. Once you’ve identified your financial goals, you can develop a plan to achieve those goals. This may involve diversifying your investments, identifying tax-efficient investment strategies, and monitoring your portfolio regularly to ensure that you’re on track to meet your goals.
Asset Management Tips and Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of asset management strategies, it’s important to follow best practices and develop good habits. One of the most important tips is to diversify your investments. By spreading your investments across different assets, you can minimize the impact of market fluctuations and reduce the risk of losing all of your investments in one fell swoop.
Another best practice is to monitor your investments regularly. This involves tracking the performance of your investments, analyzing market trends, and making adjustments as necessary. It’s also important to stay up-to-date on tax laws and regulations, as these can have a significant impact on your investment strategy.
Finally, it’s important to work with a financial advisor or asset manager to develop a comprehensive asset management plan. A professional can help you analyze your current portfolio, identify your financial goals, and develop a plan to achieve those goals. They can also provide valuable advice and guidance along the way, helping you maximize the benefits of your asset management strategy.
Asset Management Tools and Technologies
There are a variety of tools and technologies available to help you manage your investments and maximize the benefits of your asset management strategy. One popular tool is robo-advisors, which use algorithms and data analysis to provide investment advice and manage your portfolio. Another tool is online investment platforms, which allow you to manage your investments from your computer or mobile device.
Other technologies that can be useful for asset management include financial planning software, portfolio analysis tools, and online trading platforms. These tools can help you track the performance of your investments, analyze market trends, and make informed investment decisions.
Asset Management Services
If you’re looking for professional asset management services, there are a variety of options available. Full-service investment firms provide a range of services, including portfolio management, financial planning, and investment advice. Discount brokers offer lower fees but may provide fewer services. Robo-advisors offer automated investment advice and management at a lower cost.
When choosing an asset management service, it’s important to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. You should also compare fees and services to find the best option for your needs.
Conclusion: Why Asset Management Is Crucial for Wealth Maximization
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing financial landscape, asset management strategies are more important than ever. By managing your assets effectively, you can achieve your financial goals, protect your investments, and grow your wealth over the long term. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the importance of asset management is crucial for long-term financial stability. From analyzing your current portfolio to diversifying your investments, there are a variety of strategies that can help you maximize your wealth. So, take the time to develop a comprehensive asset management plan and start maximizing your wealth today.