Why Bonds are a Safe and Stable Investment for Your Portfolio
Investors are always on the hunt for a stable and reliable investment that can help them grow their wealth over the long-term. While there are many options available, one investment class that has stood the test of time is bonds. Bonds are essentially loans made to corporations or governments, and they provide a fixed rate of return over a predetermined period of time. Bonds are considered a safe and stable investment because they are less volatile than stocks and provide a steady stream of income.
In this article, we’ll explore why bonds are a smart addition to your investment portfolio and how they can help you achieve your financial goals while minimizing risk. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the benefits of bonds can help you make informed investment decisions and build a more secure financial future.
How Bonds Work
Bonds are essentially loans made to corporations or governments. When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending your money to the issuer for a fixed period of time, and in return, you receive a fixed rate of interest. Bonds have a face value, which is the amount that the issuer will pay you when the bond matures. The face value is also known as the principal.
Bonds are issued in denominations of $1,000 or more, and they typically have a maturity date of 10 years or more. When the bond matures, the issuer returns the principal to the investor. Bonds can be bought and sold on the open market, and their price can fluctuate based on various factors, such as changes in interest rates and the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Bonds are a type of debt security, meaning they represent a promise by the issuer to pay back the principal and interest to the bondholder. When you invest in bonds, you become a creditor of the issuer, and you are entitled to receive interest payments and the return of your principal when the bond matures.
Types of Bonds – Corporate, Municipal, and Government
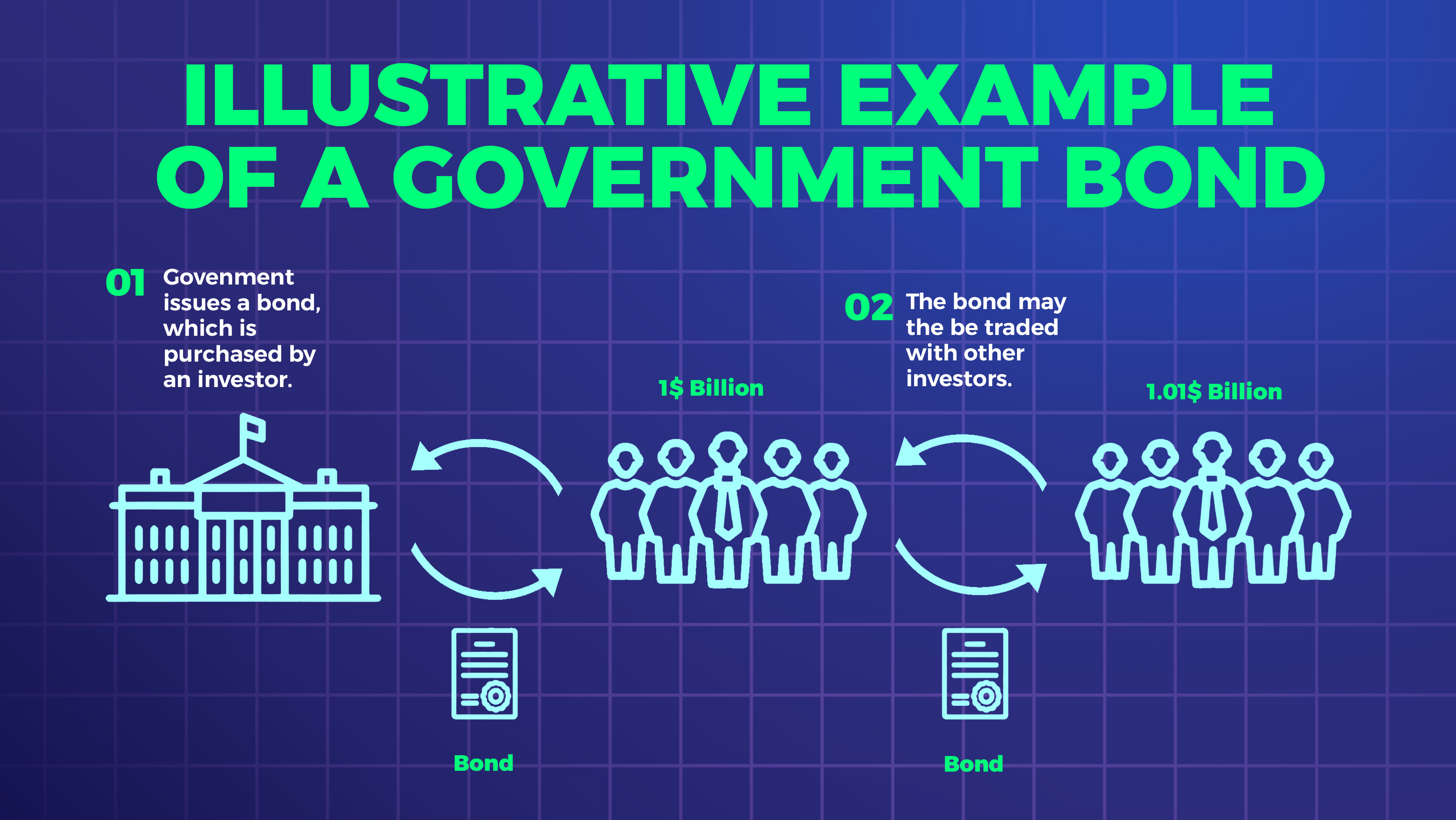
There are several types of bonds available to investors, including corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and government bonds.
Corporate bonds are issued by corporations to raise capital for various purposes, such as funding expansion or paying off debt. Corporate bonds are generally considered riskier than government bonds because they are not backed by the full faith and credit of the government.
Municipal bonds, also known as “munis,” are issued by state and local governments to fund various projects, such as building schools or roads. Municipal bonds are generally considered less risky than corporate bonds because they are backed by the taxing authority of the issuer.
Government bonds, also known as Treasury bonds, are issued by the federal government to fund its operations. Government bonds are considered the safest type of bonds because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
Benefits of Investing in Bonds – Stability, Regular Income, and Diversification
One of the main benefits of investing in bonds is their stability. Unlike stocks, which can be highly volatile and subject to significant fluctuations, bonds provide a steady stream of income and are less likely to experience large swings in price. This stability makes bonds an attractive option for investors who are looking for a reliable source of income and a way to minimize risk in their portfolio.
Another benefit of investing in bonds is the regular income they provide. Unlike stocks, which generally do not pay dividends, bonds pay interest on a regular basis. This interest can be reinvested to compound returns over time, or it can be used to supplement income.
Investing in bonds can also help diversify your portfolio. By investing in a variety of assets, including stocks, bonds, and other investments, you can reduce your overall risk and potentially maximize your returns. Bonds can provide a valuable source of diversification because they tend to have a low correlation with stocks and other assets.
Unlock Wealth: Sign Up Now for Smart Investing Success
Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds – Interest Rate Risk, Credit Risk, and Inflation Risk
While bonds are generally considered a safe and stable investment, there are still risks associated with investing in them. One of the main risks is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds decreases, making them less attractive to investors. This can result in a decline in the price of the bond, which can lead to a loss of principal if the bond is sold before it matures.
Credit risk is another risk associated with investing in bonds. This refers to the risk that the issuer of the bond will default on its debt obligations, which can result in a loss of principal for the investor. The creditworthiness of the issuer is an important factor to consider when investing in bonds.
Inflation risk is another risk associated with investing in bonds. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of the investor’s money over time, and if the bond’s interest rate does not keep pace with inflation, the investor may experience a loss of purchasing power.
Understanding Bond Ratings
Bond ratings are used by credit rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s, to assess the creditworthiness of bond issuers. Bond ratings are based on various factors, such as the issuer’s financial strength, its ability to make interest and principal payments, and its overall creditworthiness.
Higher-rated bonds, such as those rated AAA or AA, are considered safer investments because they have a lower risk of default. Lower-rated bonds, such as those rated BB or B, are considered riskier investments because they have a higher risk of default.
When investing in bonds, it is important to understand the bond’s rating and to consider the creditworthiness of the issuer before making an investment.
How to Invest in Bonds – Direct Purchase, Bond Funds, and ETFs
There are several ways to invest in bonds, including direct purchase, bond funds, and ETFs.
Direct purchase involves buying bonds directly from the issuer. This can be done through a broker or directly from the issuer. Direct purchase allows investors to hold the bond until maturity and receive the full principal and interest payments.
Bond funds are professionally managed portfolios of bonds that are designed to provide investors with exposure to various types of bonds. Bond funds can provide diversification and professional management, but they also come with fees and expenses.
ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, are similar to bond funds but are traded on an exchange like a stock. ETFs can provide diversification, low fees, and flexibility, but they also come with risks, such as the risk of price fluctuations and the risk of tracking error.
Tips for Building a Bond Portfolio
When building a bond portfolio, it is important to consider several factors, such as your investment goals, time horizon, risk tolerance, and overall investment strategy. Here are some tips for building a bond portfolio:
- Determine your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Consider the types of bonds you want to invest in, such as corporate, municipal, or government bonds.
- Consider the creditworthiness of the issuer.
- Consider the bond’s maturity and interest rate.
- Consider the fees and expenses associated with the investment.
- Diversify your portfolio by investing in a variety of bonds and other assets.
Bond Investment Strategies – Ladder, Barbell, and Bullet
There are several bond investment strategies that investors can use to achieve their investment goals, such as a ladder, barbell, or bullet strategy.
A ladder strategy involves investing in a series of bonds with different maturities. This can provide a steady stream of income and reduce interest rate risk.
A barbell strategy involves investing in a combination of short-term and long-term bonds. This can provide a balance between stability and growth.
A bullet strategy involves investing in bonds with a single maturity date. This can be useful for investors who have a specific investment goal, such as saving for a child’s college education.
Conclusion – Why Bonds Should Be Part of Your Investment Portfolio
Bonds are a safe and stable investment that can provide a steady stream of income and help diversify your portfolio. While there are risks associated with investing in bonds, such as interest rate risk and credit risk, these risks can be managed through careful selection and diversification.
Investing in bonds can help you achieve your financial goals while minimizing risk, and it should be considered as part of a well-diversified investment portfolio. Whether you choose to invest in bonds directly, through bond funds, or through ETFs, understanding the benefits and risks of bonds can help you make informed investment decisions and build a more secure financial future.
