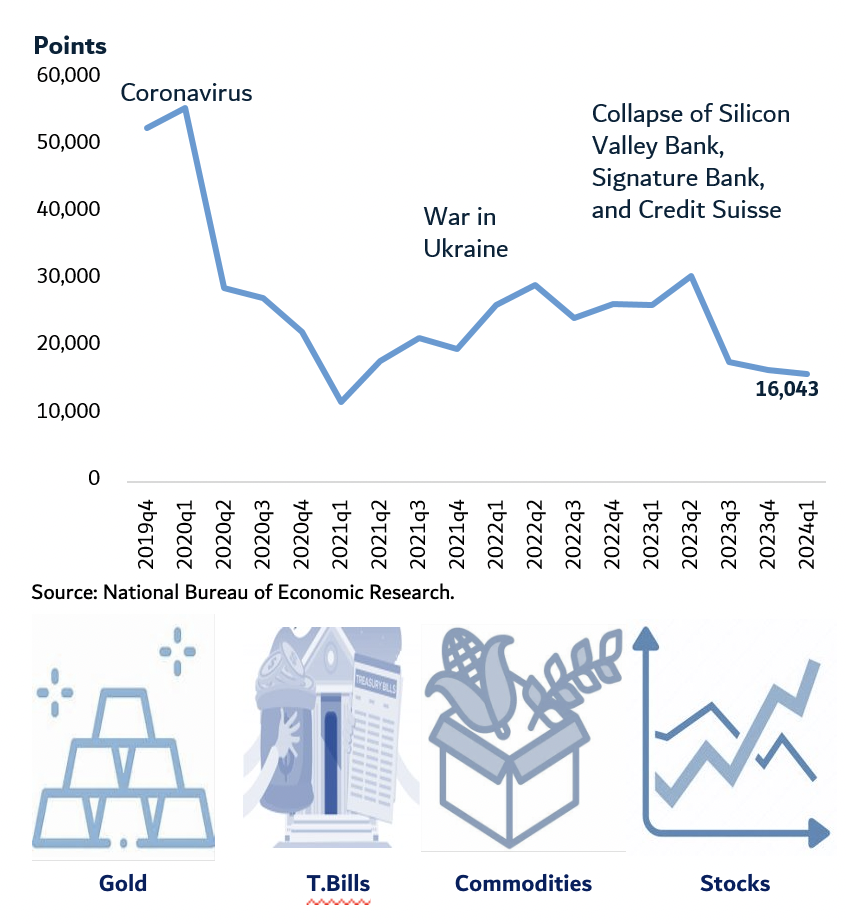
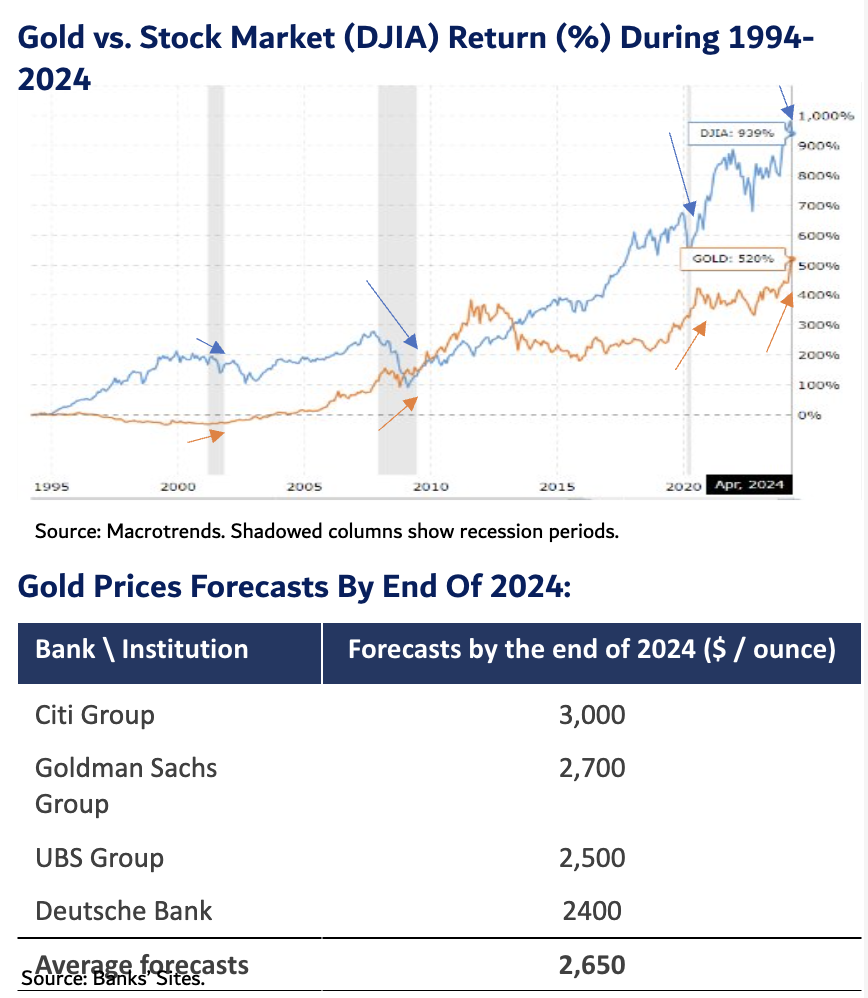
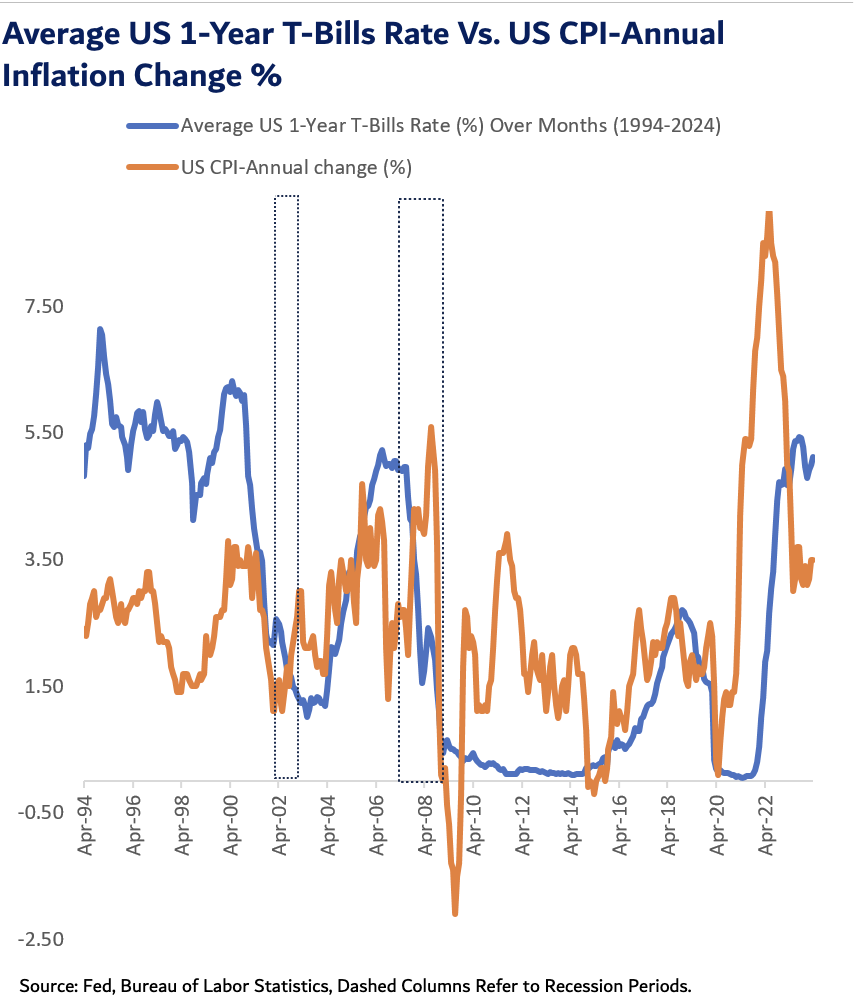
In today’s fast-paced financial world, understanding the pros and cons of physical commodities and futures contracts is crucial for investors and traders alike. Physical commodities, such as gold, oil, or agricultural products, have been considered a safe haven for centuries.
They offer tangible value and serve as a hedge against inflation. On the other hand, futures contracts provide an opportunity to speculate on the future price movements of these commodities without actually owning them. This flexibility allows traders to take advantage of price fluctuations and potentially profit from market trends. However, futures trading also carries risks, such as leverage and the potential for substantial losses.
By delving into the pros and cons of physical commodities and futures contracts, investors can make more informed decisions and tailor their strategies to their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Join us as we explore the world of physical commodities and futures contracts, uncovering the benefits and pitfalls that come with them.
What are physical commodities?
Physical commodities are tangible goods that have value and can be traded. Examples of physical commodities include gold, silver, oil, natural gas, agricultural products like wheat and corn, and even livestock.
These commodities are often used in various industries, making them essential for global economic activities. Physical commodities are attractive to investors because they offer a sense of security and stability.
Unlike paper assets, such as stocks or bonds, physical commodities have intrinsic value and can serve as a hedge against inflation. Investing in physical commodities allows investors to diversify their portfolio and protect their wealth from market volatility.
However, investing in physical commodities has its drawbacks. One of the main challenges is storage and transportation.
Commodities like gold or oil require secure storage facilities, which can be costly. Additionally, transportation costs can impact the profitability of investing in physical commodities, especially for bulk commodities like agricultural products.
Another disadvantage is the lack of liquidity compared to other financial instruments. Selling physical commodities can take time and may involve additional costs, making it less suitable for short-term trading strategies.
Despite these challenges, physical commodities remain an attractive option for long-term investors looking for stability and a tangible store of value.
Pros of investing in physical commodities
Investing in physical commodities offers several advantages. Firstly, physical commodities provide a hedge against inflation. As the value of paper currencies fluctuates, physical commodities tend to retain their value or even appreciate in price.
This makes them a reliable store of wealth over the long term. Secondly, physical commodities have a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks or bonds. This means that adding physical commodities to a diversified portfolio can help reduce overall risk and increase stability. Lastly, physical commodities are tangible assets.
Unlike stocks or bonds, investors can physically hold their investments, giving them a sense of security and control.
Unlock Wealth: Sign Up Now for Smart Investing Success
Cons of investing in physical commodities
While physical commodities have their benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Storage and transportation costs can eat into investment returns, especially for bulk commodities that require specialized facilities.
Additionally, physical commodities are subject to supply and demand dynamics. Changes in global production, geopolitical events, or weather conditions can impact the price and availability of physical commodities. This volatility can lead to price fluctuations and potential losses for investors.
Lastly, physical commodities lack the income-generating potential of other assets. Unlike dividends from stocks or interest payments from bonds, physical commodities do not provide regular cash flow. Investors must rely on price appreciation to generate returns.
What are futures contracts?
Futures contracts are financial derivatives that allow investors to speculate on the future price movements of physical commodities without owning the underlying asset.
A futures contract is an agreement between a buyer and a seller to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a predetermined price and date in the future.
Futures contracts are traded on exchanges, providing liquidity and ease of trading. This makes futures contracts an attractive option for short-term traders looking to profit from price fluctuations.
Pros of investing in futures contracts
One of the main advantages of investing in futures contracts is the ability to speculate on the price movements of physical commodities without owning them. This allows traders to take advantage of both rising and falling markets. With the use of leverage, traders can control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, potentially amplifying their returns.
Additionally, futures contracts offer liquidity and transparency. Trading takes place on regulated exchanges, ensuring fair pricing and ease of execution. This makes futures contracts suitable for short-term trading strategies and hedging against price volatility.
Cons of investing in futures contracts
While futures contracts offer potential rewards, they also come with inherent risks. Leverage, which allows traders to control larger positions with borrowed money, can amplify both gains and losses. This means that even a small adverse price movement can result in substantial losses.
Futures trading also requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to accurately predict price movements. Without proper knowledge and analysis, traders may make poor investment decisions and suffer significant losses.
Additionally, futures contracts have expiration dates, which means traders need to actively monitor their positions and roll over contracts to avoid physical delivery or potential losses.
Key differences between physical commodities and futures contracts
Physical commodities and futures contracts have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Physical commodities offer tangible value and serve as a store of wealth, while futures contracts are financial derivatives that offer speculative opportunities.
Physical commodities require storage and transportation, while futures contracts are traded on exchanges and do not involve physical ownership. Physical commodities provide long-term stability and inflation protection, while futures contracts offer short-term trading opportunities and potential leverage. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors to determine which investment avenue aligns with their goals and risk tolerance.
Considerations before investing in physical commodities or futures contracts
Before investing in physical commodities or futures contracts, several factors should be considered. Firstly, investors should assess their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Physical commodities offer stability and long-term value appreciation, while futures contracts offer potential short-term gains but come with higher risks. Secondly, investors should evaluate their knowledge and expertise in the respective markets.
Investing in physical commodities may require understanding supply and demand dynamics, global trends, and geopolitical factors. Futures trading demands technical analysis skills and the ability to interpret market indicators. Lastly, investors should consider their time horizon.
Physical commodities are suitable for long-term investors, while futures contracts are more suitable for short-term traders.
Conclusion
Understanding the pros and cons of physical commodities and futures contracts is essential for investors and traders seeking to navigate the financial markets effectively.
Physical commodities offer stability, a hedge against inflation, and tangible value. However, they come with challenges such as storage costs and lack of liquidity.
Futures contracts provide the opportunity to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset, offering leverage and liquidity. However, futures trading carries risks, including leverage and the need for market expertise.
By carefully considering these factors and aligning them with their investment goals and risk tolerance, investors can make informed decisions and tailor their strategies to optimize their returns.
Whether it’s the allure of physical commodities or the excitement of futures contracts, understanding the benefits and pitfalls is crucial for successful investing.