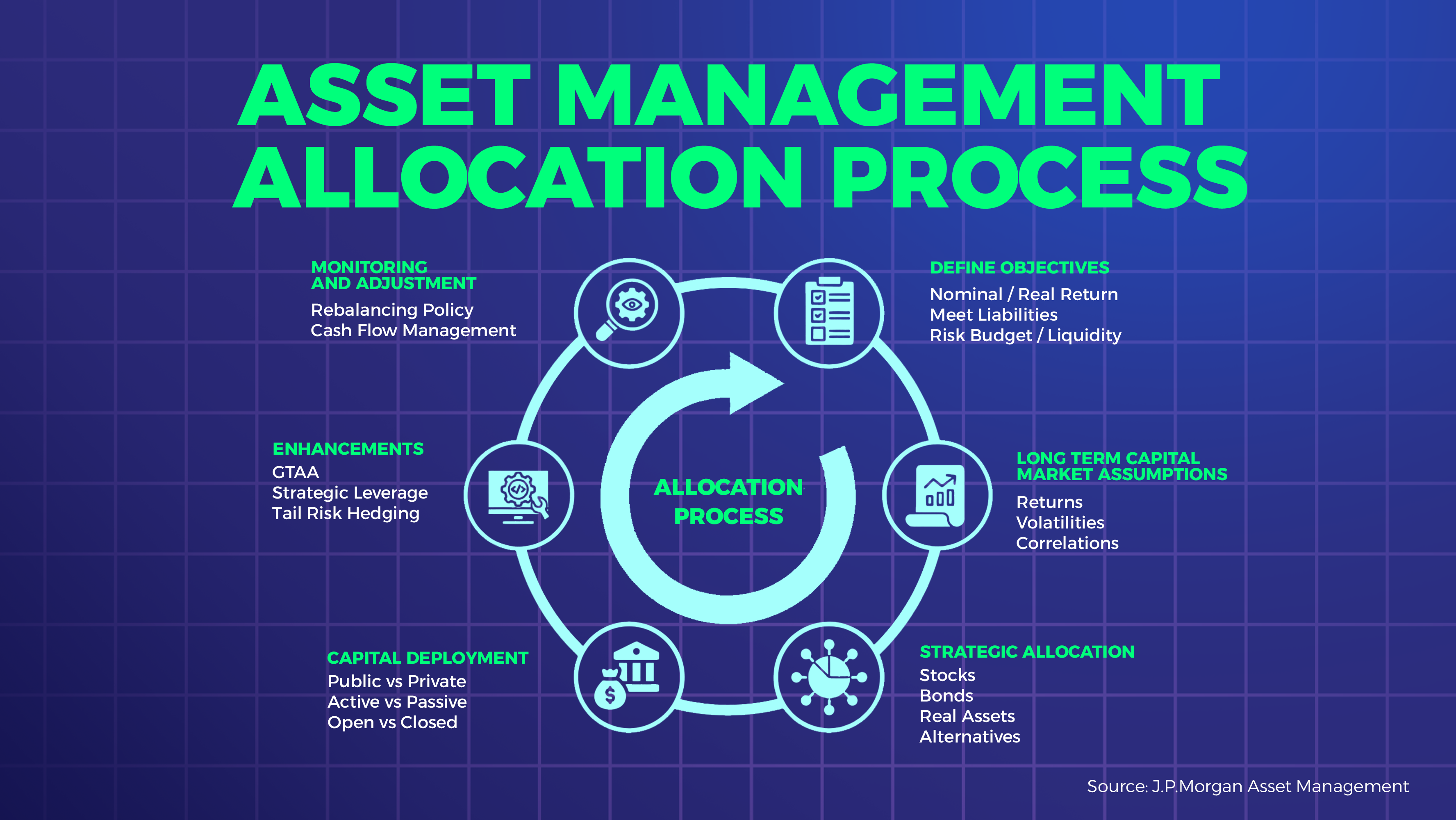
Asset management is a crucial part of any investment strategy. The right asset management strategy is essential to ensure that you achieve your financial goals while effectively managing risks.
When choosing an asset management strategy, it’s essential to consider some key factors such as your financial goals and risk tolerance. This will help you choose a strategy that aligns with your objectives and allows you to maximize returns while minimizing risks.
Key Takeaways:
1- Choosing the right asset management strategy is crucial to achieving your financial goals.
2- When selecting a strategy, consider your risk tolerance and financial objectives.
3- Asset allocation and diversification are key components of an effective asset management strategy.
4-Effective monitoring and regular review are essential for the success of your asset management strategy.
Understanding Asset Management
Asset management is a process of managing your financial assets, such as investment portfolios, to achieve your investment objectives. Asset managers are professionals who use various strategies to manage their clients’ investments effectively.
Asset management involves the careful selection of financial instruments and the monitoring of those investments to ensure they align with the clients’ goals. It also involves risk assessment, diversification, and asset allocation, which are crucial components of an effective asset management strategy.
“Asset management is not about beating the market; it’s about achieving your financial goals with the least amount of risk possible”
Asset management involves creating an investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. In the next sections, we will explore the essential components of an effective asset management strategy and how you can select the right strategy that works for you.
Assessing Your Financial Goals
Determining your financial goals and investment objectives is an essential step in selecting the right asset management strategy. It helps you design a portfolio that aligns with your long-term goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Before investing, ask yourself what you want to achieve with your investments, what timeline you have in mind, and how much risk you’re willing to take.
You can start by identifying your short-term goals, such as paying off a debt or building an emergency fund, then move on to long-term goals, like saving for a down payment or retirement. It’s best to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that you can track and adjust over time.
When assessing your financial goals, consider your current financial situation, your income, expenses, and debt, as well as any expected changes in the future. Also, consider your age, your family status, and your expected retirement age. These factors may affect your investment choices and the level of risk you’re comfortable with.
Evaluating Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to the degree of risk an individual is willing to undertake when investing. It is determined by various factors, including age, income, personal circumstances, and investment goals. It is essential to evaluate your risk tolerance before choosing an asset management strategy.
Risk assessment is the process of identifying and analyzing potential risks associated with an investment. It helps investors understand the potential downside of an investment and manage their risks effectively.
Understanding risk appetite is another critical factor when evaluating risk tolerance. Risk appetite refers to the level of risk an investor is willing to take on to achieve their investment goals. It is important to strike a balance between risk and reward when choosing an asset management strategy.
Based on your risk assessment and risk appetite, you can select an asset management strategy that aligns with your investment goals and objectives. It is essential to understand that a high-risk investment may yield high returns, but it also carries a higher level of uncertainty and volatility. A low-risk investment may provide more stability but with lower returns.
The right asset management strategy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It depends on various factors, including your financial goals, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. Evaluating your risk tolerance is a crucial step towards selecting the right asset management strategy.
Types of Asset Management Strategies
When it comes to asset management, there are a variety of strategies to choose from. Each strategy has its pros and cons, and investors should consider their financial goals and risk tolerance before selecting a strategy. In this section, we will explore some of the most common types of asset management strategies.
Active Management
Active management is a hands-on approach where fund managers use their expertise to make investment decisions actively. This strategy involves constant monitoring and adjustments of investments to maximize returns. While active management can result in higher returns, it also comes with higher fees and increased risks.
Passive Management
Passive management, also known as index investing, aims to replicate the performance of a particular market index. This strategy involves investing in a diversified portfolio of assets that mirror the composition of the index. Passive management typically has lower fees and is less risky than active management but may not offer the same potential for high returns.
Specialized Approaches
Other specialized approaches include factor investing, which focuses on specific risk factors, such as value or momentum, and socially responsible investing, which considers environmental, social, and governance factors in investment decisions. These strategies cater to investors with specific investment objectives and preferences and can be an effective way to align investments with personal values.
It’s essential to consider all available types of asset management strategies before making an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Remember, diversification is critical, and combining different strategies may be the right approach to a successful asset management plan.
Considering Diversification and Asset Allocation
Diversification and asset allocation are essential components of an effective asset management strategy. Diversification is the practice of investing in a variety of assets to reduce the overall risk of your portfolio. Asset allocation is the process of dividing your investments among different categories of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to optimize returns.
When choosing an asset management strategy, it’s crucial to consider diversification and asset allocation. By spreading your investments across a variety of assets, you can mitigate risks and reduce potential losses. Asset allocation allows you to optimize your returns by investing in assets that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
One popular approach to diversification and asset allocation is to invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), which provide exposure to a diverse range of assets in a single investment. Another approach is to invest in individual stocks and bonds across different industries and sectors. Both approaches have pros and cons, and the best option for you will depend on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
The Importance of Rebalancing
Once you have established your diversification and asset allocation strategy, it’s important to regularly monitor and rebalance your portfolio. Rebalancing involves adjusting your investments to maintain your desired asset allocation. Over time, certain assets may perform better or worse than others, causing your portfolio to stray from your original allocation.
Rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. It also allows you to capitalize on market fluctuations and take advantage of opportunities to buy low and sell high.
| Benefits of Diversification and Asset Allocation |
| Reduces the overall risk of your portfolio |
| Optimizes returns by investing in assets that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance |
| Allows you to capitalize on market fluctuations and take advantage of opportunities to buy low and sell high |
Overall, diversification and asset allocation are crucial to building a successful asset management strategy. By spreading your investments across a variety of assets and optimizing your portfolio allocation, you can mitigate risks and maximize returns. Remember to regularly monitor and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Effective Implementation and Monitoring
Choosing the right asset management strategy is just the first step towards achieving your financial goals. Once you have selected an appropriate strategy, it’s important to effectively implement and monitor your investment portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with your objectives.
Regular monitoring can help you track the performance of your portfolio and evaluate whether it’s meeting your expectations. It’s essential to review your portfolio periodically and make any adjustments as needed to optimize performance and mitigate risks.
When monitoring your portfolio, you should pay close attention to the asset allocation and diversification of your investments. These factors play a significant role in determining the risk and return of your portfolio. You should also keep an eye on market conditions and industry trends that may impact your investments.
It’s crucial to have an effective implementation plan in place to ensure your investment strategy is executed correctly. This includes identifying the right investment products and services, establishing a timeline for investment, and managing the associated costs.
Finally, ongoing review and adjustments are necessary to ensure your investment strategy remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Regular check-ins with a financial advisor or asset management team can provide valuable insights and recommendations for necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Choosing the right asset management strategy is the foundation of building a strong financial future. By understanding what asset management entails and assessing your financial goals and risk tolerance, you can choose a strategy that aligns with your needs.
Consider the various types of asset management strategies available, including active and passive management, and other specialized approaches. Evaluate the importance of diversification and asset allocation in mitigating risks and maximizing returns.
Effective Implementation and Monitoring
Once you have chosen your asset management strategy, it’s crucial to implement and monitor it effectively. Regularly track the performance of your portfolio, review it, and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that it remains on track to meet your goals.
Remember, implementing and monitoring your asset management strategy is an ongoing process that requires your attention. By staying on top of your investments, you can ensure that your strategy remains aligned with your financial goals.
With these steps in mind, you are now equipped with the knowledge to make an informed decision about choosing the right asset management strategy for your needs. By taking a thoughtful approach to your investments, you can build a strong financial foundation for the future.
FAQ
Q: How do I choose the right asset management strategy?
A: When selecting an asset management strategy, it’s important to consider your financial goals and risk tolerance. By assessing these factors, you can choose a strategy that aligns with your objectives.
Q: What is asset management and why is it important?
A: Asset management involves effectively managing your financial assets and investment portfolios. It is important because it helps you optimize your investments and achieve your financial goals.
Q: How do I assess my financial goals?
A: Assessing your financial goals involves identifying your investment objectives and long-term goals. By understanding your goals, you can select an asset management strategy that supports your desired outcomes.
Q: Why is evaluating risk tolerance important?
A: Evaluating your risk tolerance is important because it determines your comfort level with investment risks. By understanding your risk tolerance, you can choose an asset management strategy that aligns with your risk appetite.
Q: What are the different types of asset management strategies?
A: There are various types of asset management strategies, including active management, passive management, and other specialized approaches. Each strategy has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Q: Why is diversification and asset allocation important in asset management?
A: Diversification and asset allocation are important because they help mitigate risks and maximize returns. By diversifying your investments and optimizing asset allocation, you can create a well-balanced investment portfolio.
Q: How do I effectively implement and monitor my asset management strategy?
A: To effectively implement and monitor your asset management strategy, you should track the performance of your portfolio, regularly review it, and make adjustments as necessary. This ensures your strategy remains aligned with your goals.
Q: Conclusion
A: Selecting the right asset management strategy is crucial for achieving your financial goals. By considering your financial goals, risk tolerance, and understanding different asset management strategies, you can make an informed decision. Remember to implement your strategy effectively and monitor it regularly for optimal results.