Asset management is the process of managing a company’s or individual’s investments to achieve specific financial goals while minimizing risk.
This includes a range of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
Asset management typically involves working with a professional asset manager, who uses a variety of techniques to analyze financial data,
identify opportunities for investment, and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources.
These decisions may involve selecting individual securities or investment products, setting investment strategies, and monitoring the performance of the portfolio over time.
Effective asset management requires a deep understanding of financial markets, investment products, and risk management techniques,
as well as strong analytical and communication skills. It is an important tool for individuals and businesses looking to grow their wealth, manage their assets, and achieve their financial goals over the long term.
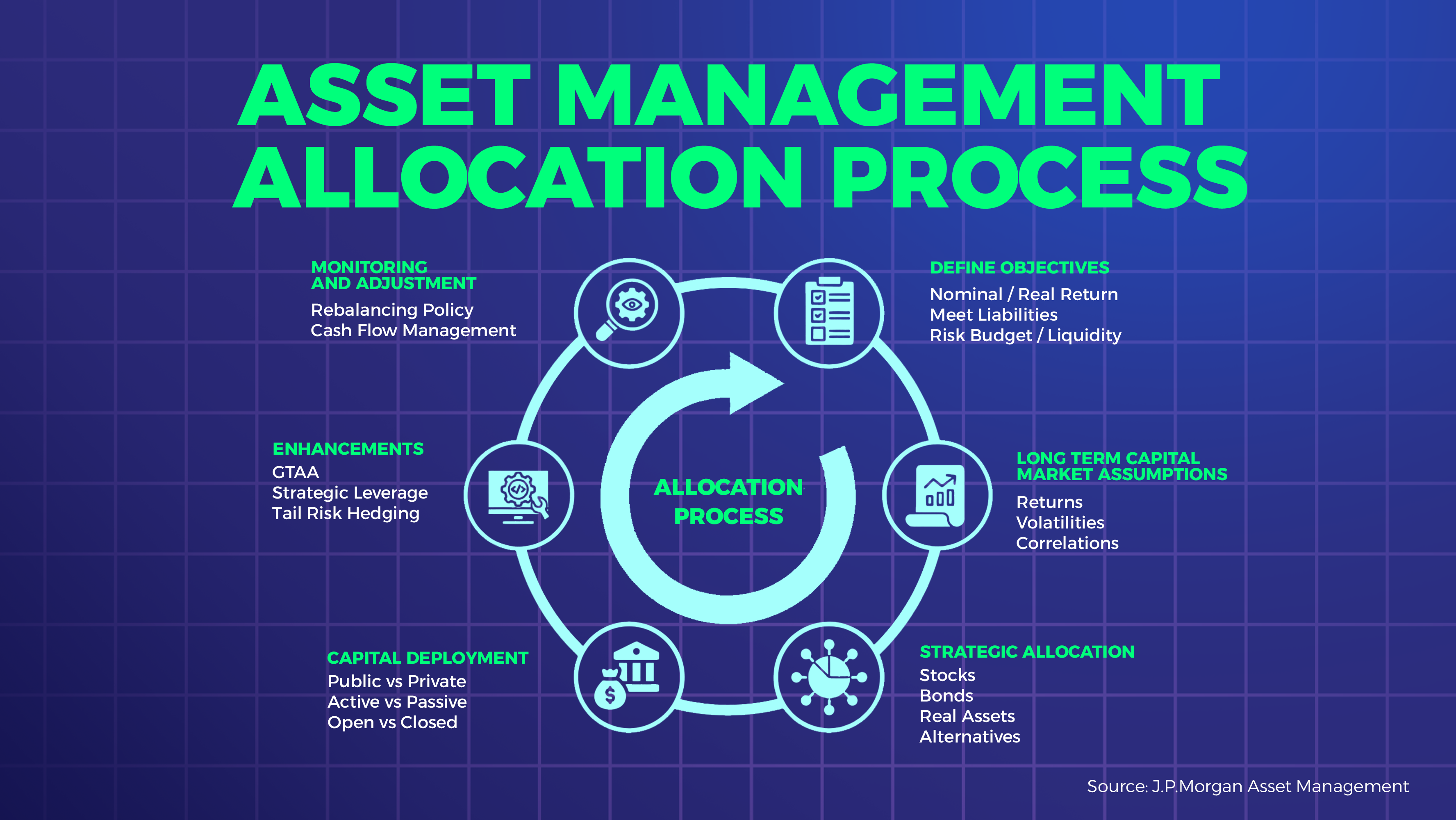
Types of Asset Managers
There are several types of asset managers, each specializing in managing different types of assets and catering to different types of clients.
Here are some of the most common types:
Investment Managers: These asset managers manage investment portfolios on behalf of their clients.
They are responsible for selecting individual securities and making investment decisions based on market analysis and their clients’ investment goals.
Wealth Managers: Wealth managers provide comprehensive financial planning and investment management services to high-net-worth individuals and families.
They help their clients manage their wealth by creating personalized investment strategies, tax planning, estate planning, and more.
Hedge Fund Managers: Hedge fund managers manage funds that invest in a variety of financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and derivatives.
They aim to generate high returns for their clients by using sophisticated investment strategies and taking on higher levels of risk.
Private Equity Managers: Private equity managers manage funds that invest in privately held companies.
They aim to generate high returns for their investors by buying and selling companies, restructuring businesses, and improving operational efficiency.
Real Estate Asset Managers: Real estate asset managers manage portfolios of real estate investments on behalf of their clients.
They are responsible for selecting properties, managing the properties, and maximizing their clients’ returns.
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) Managers: ETF managers create and manage ETFs, which are investment funds traded on stock exchanges.
They are responsible for selecting the underlying assets, managing the portfolio, and tracking the performance of the ETF.
Mutual Fund Managers: Mutual fund managers manage mutual funds, which are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest
in a diversified portfolio of assets. They are responsible for selecting the individual securities in the portfolio, managing the portfolio, and tracking the performance of the fund.
These are just a few examples of the types of asset managers that exist. Each type of asset manager has its unique set of skills, expertise, and investment strategies that cater to different types of clients and investment goals.
How Much Does Asset Management Cost?
The cost of asset management can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the type and size of assets being managed, the investment strategy employed, the level of service provided by the asset manager, and the fee structure used.
Typically, asset management fees are charged as a percentage of assets under management (AUM).
The average fee for asset management services is around 1% of AUM per year, but this can vary widely depending on the factors mentioned above.
For example, some asset managers may charge a higher fee for actively managed portfolios that require more research and analysis,
while others may charge a lower fee for passive or index-based strategies. Additionally, some asset managers may offer different levels of service
such as personalized financial planning or tax advice, which can also affect the cost.
It’s important to carefully review the fee structure and any other associated costs before choosing an asset manager. It’s also a good idea to consider.
The potential benefits of professional asset management, such as access to expertise and diversified investment portfolios, when evaluating the costs.
How Asset Management Companies Work
Asset management companies are financial institutions that manage and invest the assets of individuals and institutions.
These companies offer a range of investment services, including managing portfolios of stocks, bonds, and other securities on behalf of clients.
Here’s a general overview of how asset management companies work:
Client Onboarding: Asset management companies begin by identifying potential clients and evaluating their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and financial situation. They then develop investment strategies that align with the client’s goals.
Portfolio Management: Once a client’s investment objectives and risk tolerance have been established,
Asset management companies create and manage a portfolio of assets that aligns with the client’s investment strategy.
They make investment decisions on behalf of clients, monitor the performance of the portfolio, and adjust the portfolio as needed to achieve the client’s investment goals.
Investment Research: Asset management companies conduct extensive research to identify investment opportunities that align with their clients’ objectives. They analyze financial statements, economic trends, and industry reports to make informed investment decisions.
Risk Management: Asset management companies employ risk management strategies to reduce the potential for losses in their clients’ portfolios.
This may include diversifying the portfolio across different asset classes and investment styles, monitoring market trends and making adjustments as needed, and implementing hedging strategies.
Reporting and Communication: Asset management companies provide regular reports to their clients that detail the performance of their portfolios, investment decisions made on their behalf, and any changes to their investment strategy.
They also communicate with clients on a regular basis to ensure that their investment objectives and risk tolerance remain aligned with their clients’ goals.
Overall, asset management companies play a critical role in helping individuals and institutions manage their investments and achieve their financial goals.
Example of an Asset Management Institution
An example of an asset management institution is BlackRock, Inc. BlackRock is a multinational investment management corporation headquartered in New York City.
The company offers a wide range of investment products and services, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and institutional separate accounts.
BlackRock manages assets for both individual and institutional investors, and its clients include governments, corporations, and pension funds. As of 2021,
BlackRock has over $9 trillion in assets under management (AUM), making it the largest asset management company in the world.
How Does an Asset Management Company Differ From a Brokerage?
An asset management company and a brokerage are both financial service providers, but they differ in their functions and services.
An asset management company is a financial institution that manages investments on behalf of its clients, including individuals, corporations, and institutions.
The primary goal of an asset management company is to generate returns for their clients by investing their money in various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
The asset management company typically charges a management fee based on a percentage of the assets under management,
and they may also earn performance-based fees if they achieve a certain level of return.
In contrast, a brokerage firm is a financial institution that acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers of financial securities, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The primary function of a brokerage firm is to execute trades on behalf of their clients
Typically charging a commission or a transaction fee for each trade. Brokerage firms may also offer investment advice and research, as well as other financial services such as banking and insurance.
While both asset management companies and brokerage firms provide financial services,
The key difference is that asset management companies focus on managing investments and generating returns for their clients,
while brokerage firms focus on executing trades and providing investment advice. Additionally,
asset management companies typically work with clients on a long-term basis,
while brokerage firms may have more transactional relationships with clients who trade frequently.
What Does an Asset Manager Do?
An asset manager is a professional who manages financial assets and investments on behalf of their clients.
The main responsibility of an asset manager is to maximise the return on investment while minimizing the risk for their clients.
Asset managers work with a variety of financial products, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
They analyse market trends and economic data to make informed investment decisions that align with their clients’ goals and risk tolerance.
Some common tasks that asset managers perform include:
Creating investment strategies: Asset managers create investment strategies tailored to their clients’ financial objectives and risk tolerance.
They also monitor market conditions and adjust their strategies as needed.
Portfolio management: Asset managers manage their clients’ portfolios by selecting and monitoring specific investments.
They also buy and sell assets to achieve the desired asset allocation and returns.
Risk management: Asset managers analyze the risks associated with different investments and manage those risks to protect their clients’ assets.
Research: Asset managers conduct research on different investment opportunities to identify potential risks and returns.
Client communication: Asset managers communicate with their clients regularly to keep them informed about their investments’
performance and any changes made to their portfolios.
Overall, an asset manager plays a critical role in helping individuals and organizations manage their financial assets and investments effectively.
What Are The Top Asset Management Institutions?
State Street Global Advisors
Fidelity Investments
Allianz Global Investors
JPMorgan Chase
Goldman Sachs Asset Management
UBS Asset Management
Capital Group
PIMCO
These companies manage trillions of dollars in assets and provide investment management services to a wide range of clients, including individuals,
institutional investors, and governments. They use various investment strategies to achieve their clients’ goals, such as active management, passive management, and alternative investments.

