
Join the Prestigious, Award-Winning Regional Investment Titan Today!
Flexible trading, unlimited possibilities – Trade FX, Metals, Futures, Energy, and Indices
DISCOVER WHO WE ARE
Experience and Dedications since 2007
Mubasher Capital empowers you to invest in a wide range of financial instruments, including Equities, ETFs, Options, Forex, Commodities, Indices, Bonds, Sukuk, mutual funds and more.
Our team of seasoned experts are dedicated to guiding you throughout your entire investment journey.



Award Winning Trading Platforms
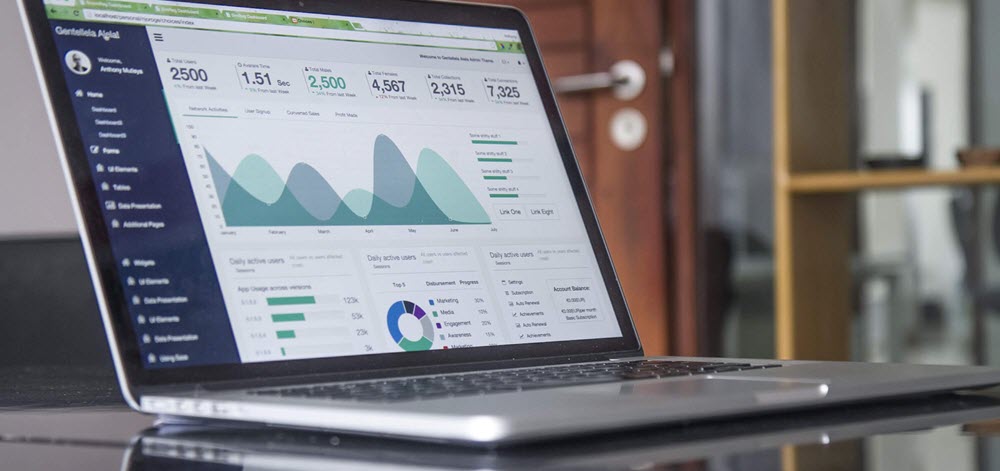
Our world-class charting tools enable you to analyze market data and make informed trading decisions, while our positions and portfolio reports provide you with a comprehensive overview of your trading activity.
Our platform boasts a range of value-added features and functions, such as real-time news and analysis, customizable alerts, and risk management tools, to help you stay ahead of the game
Copy Trading
Copy professional’s traders’ strategies with Just a click
Trade 24/7
Bring all markets data to one place.
Data Driven
Bring all markets data to one place.
Financial Target
Help Our Clients to get their Financial Freedom.
ACHIEVEMENTS


Since 2007 in The Financial Markets Industry



Invest with us
Unlike other online platforms, Mubasher Capital provides you access to multi markets, and asset classes through a single account.

Unlock Wealth: Sign Up Now for Smart Investing Success!
Learn
ACADEMY


Fixed Income Investment Strategies

Corporate Bonds Guide



